When I wrote part I of this post, I naively assumed this would only be a two-part series. However, so many great questions and comments emerged from the discussion that I realize it’s worth spending much more time on this important and misunderstood topic. In terms of setting expectations, I suspect this series will require at least four parts.
So, back to the topic at hand…. (You may want to read or maybe reread part I for a biochemistry refresher before diving into part II.)
Is there a “metabolic advantage” to being in ketosis?
Few topics in the nutrition blogosphere generate so much vitriolic rhetoric as this one, and for reasons I can’t understand. I do suspect part of the issue is that folks don’t understand the actual question. I’ve used the term “metabolic advantage” because that’s so often what folks write, but I’m not sure it has a uniform meaning, which may be part of the debate. I think what folks mean when they argue about this topic is fat partitioning, but that’s my guess. To clarify the macro question, I’ve broken the question down into more well-defined chunks.
Does ketosis increase energy expenditure?
I am pretty sure when the average person argues for or against ketosis having a “metabolic advantage” what they are really arguing is whether or not, calorie-for-calorie, a person in ketosis has a higher resting energy expenditure. In other words, does a person in ketosis expend more energy than a person not in ketosis because of the caloric composition of what they consume/ingest?
Let me save you a lot of time and concern by offering you the answer: The question has not been addressed sufficiently in a properly controlled trial and, at best, we can look to lesser controlled trials and clinical observations to a make a best guess. Believe me, I’ve read every one of the studies on both sides of the argument, especially on the ‘no’ side, including this one by Barry Sears from which everyone in the ‘no’ camp likes to quote. This particular study sought to compare a non-ketogenic low carb (NLC) diet to a ketogenic low carb (KLC) diet (yes, saying ‘ketogenic’ and ‘low carb’ is a tautology in this context). Table 3 in this paper tells you all you need to know. Despite the study participants having food provided, the KLC group was not actually in ketosis as evidenced by their B-OHB levels. At 2-weeks (of a 6-week study) they were flirting with ketosis (B-OHB levels were 0.722 mM), but by the end of the study they were at 0.333 mM. While the difference between the two groups along this metric was statistically significant, it was clinically insignificant. That said, both groups did experience an increase in REE: about 86 kcal/day in the NLC group and about 139 kcal/day in the KCL group (this is calculated using the data in Table 3 and Table 2). These changes represented a significant increase from baseline but not from each other. In other words, this study only showed that reducing carbohydrate intake increased TEE but did not settle the ‘dose-response’ question.
This study by Sears et al. is a representative study and underscores the biggest problems with addressing this question:
- Dietary prescription (or adherence), and
- Ability to accurately measure differences in REE (or TEE).
Recall from a previous post, where I discuss the recent JAMA paper by David Ludwig and colleagues, I explain in detail that TEE = REE + TEF + AEE.
Measuring TEE is ideally done using doubly-labeled water or using a metabolic chamber, and the metabolic chamber is by far the more accurate way. A metabolic chamber is a room, typically about 30,000 liters in volume, with very sensitive devices to measure VO2 and VCO2 (oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced) to allow for what is known as indirect calorimetry. The reason this method is indirect is that it calculates energy expenditure indirectly from oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production rather than directly via heat production. By comparison, when scientists need to calculate the energy content of food (which they do for such studies), the food is combusted in a bomb calorimeter and heat production is measured. This is referred to as direct calorimetry.
Subjects being evaluated in such studies will typically be housed in a metabolic ward (don’t confuse a metabolic ward with a metabolic chamber; the ward is simply a fancy hospital unit; the chamber is where the measurements are made) under strict supervision and every few days will spend an entire 24 hour period in one such chamber in complete isolation (so no other consumption of oxygen or production of carbon dioxide will interfere with the measurement). This is the ‘gold standard’ for measuring TEE, and shy of doing this it’s very difficult to measure differences within about 300 kcal/day.
Not surprisingly, virtually no studies use metabolic chambers and instead rely on short-term measurement of REE as a proxy. In fact, there are only about 14 metabolic chambers in the United States.
A broader question, which overlays this one, is whether any change in macronutrients impacts TEE.
Despite the limitations we allude to in the summary of this review, there is a growing body of recent literature (for example this study, this study, and this study) that do suggest a thermogenic effect, specifically, of a ketogenic diet, possibly through fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21) which increases with B-OHB production by the liver.
These mice studies (of course, what is true in mice isn’t necessarily true in humans, but it’s much easier to measure in mice) show that FGF21 expression in the liver is under the control of the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor a (PPARa), which is activated during starvation. Increased FGF21 promotes lipolysis in adipose tissue and the release of fatty acids into the circulation. Fatty acids are then taken up by the liver and converted into ketone bodies. FGF21 expression in liver and adipose tissue is increased not only by fasting but also by a high fat diet as well as in genetic obesity which, according to these studies, may indicate that increased FGF21 expression may be protective. Hence, ketosis may increase TEE either by increasing REE (thermogenic) or AEE (the ketogenic mice move more). Of course, this does not say why. Is the ketogenic diet, by maximally reducing insulin levels, maximally increasing lipolysis (which dissipates energy via thermogenic and/or activity ‘sinks’) or is the ketogenic diet via some other mechanism increasing thermogenesis and activity, and the increased lipolysis is simply the result? We don’t actually know yet.
Bottom line: There is sufficient clinical evidence to suggest that carbohydrate restriction may increase TEE in subjects, though there is great variability across studies (likely due the morass of poorly designed and executed studies which dilute the pool of studies coupled with the technical difficulties in measuring such changes) andwithin subjects (look at the energy expenditure charts in this post). The bigger question is if ketosis does so to a greater extent than would be expected/predicted based on just the further reduction in carbohydrate content. In other words, is there something “special” about ketosis that increases TEE beyond the dose effect of carbohydrate removal? That study has not been done properly, yet. However, I have it on very good authority that such a study is in the works, and we should have an answer in a few years (yes, it takes that long to do these studies properly).
Does ketosis offer a physical performance advantage?
Like the previous question this one needs to be defined correctly if we’re going to have any chance at addressing it. Many frameworks exist to define physical performance which center around speed, strength, agility, and endurance. For clarity, let’s consider the following metrics which are easy to define and measure
- Aerobic capacity
- Anaerobic power
- Muscular strength
- Muscular endurance
There are certainly other metrics against which to evaluate physical performance (e.g., flexibility, coordination, speed), but I haven’t seen much debate around these metrics.
To cut to the chase, the answers to these questions are probably as follows:
- Does ketosis enhance aerobic capacity? Likely
- Does ketosis enhance anaerobic power? No
- Does ketosis enhance muscular strength? Unlikely
- Does ketosis enhance muscular endurance? Likely
Why? Like the previous question about energy expenditure, addressing this question requires defining it correctly. The cleanest way to define this question, in my mind, is through the lens of substrate use, oxygen consumption, and mechanical work.
But this is tough to do! In fact, to do so cleanly requires a model where the relationship between these variables is clearly defined. Fortunately, one such model does exist: animal hearts. (Human hearts would work too, but we’re not about to subject humans to these experiments.) Several studies, such as this, this, and this, have described these techniques in all of their glorious complexities. To fully explain the mathematics is beyond the scope of this post, and not really necessary to understand the point. To illustrate this body of literature, I’ll use this article by Yashihiro Kashiwaya et al.
The heart is studied because the work action is (relatively) simple to measure: cardiac output, which is the product of stroke volume (how much blood the heart pumps out per beat) and heart rate (how many times the heart beats per minute). One can also measure oxygen consumption, all intermediate metabolites, and then calculate cardiac efficiency. Efficiency increases as work increases relative to oxygen consumption.
Before we jump into the data, you’ll need to recall two important pieces of physiology to “get” this concept: the acute (vs. chronic) metabolic effect of insulin, and the way ketone bodies enter the Krebs Cycle.
The acute metabolic effects of insulin are as follows:
- Insulin promotes translocation (movement from inside the cell to the cell membrane) of GLUT4 transporters, which facilitate the flux of glucose from the plasma into the inside of the cell.
- Insulin drives the accumulation of glycogen in muscle and liver cells, when there is capacity to do so.
- Least known by most, insulin stimulates the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) inside the mitochondria, thereby increasing the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (see figure below).
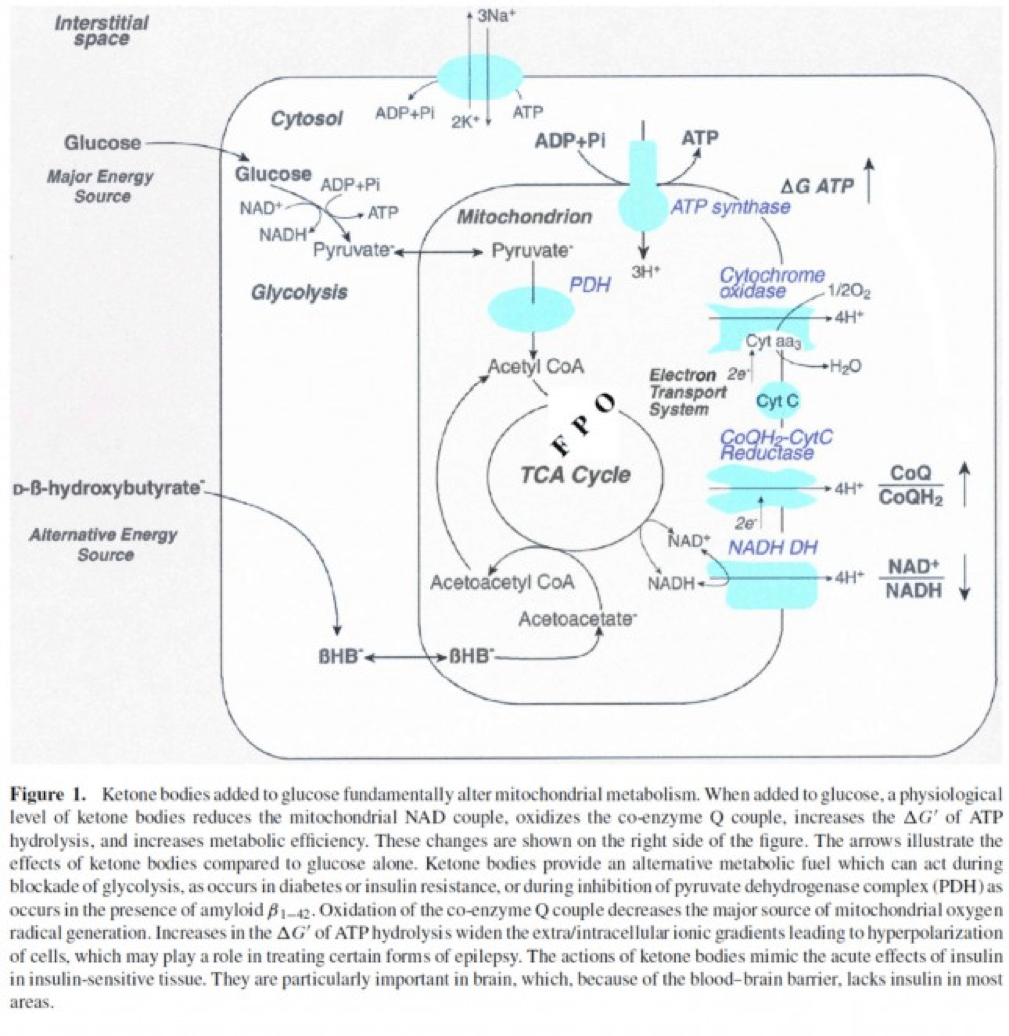
The second important point to recall is that ketone bodies bypass this process (i.e., glucose to pyruvate to acetyl CoA), as B-OHB enters the mitochondria, converts into acetoacetate, and enters the Krebs Cycle directly (between succinyl CoA and succinate, for any biochem wonks out there). I keep alluding to this distinction for a reason that will become clear shortly.
An elegant way to test the relative impact of glucose, insulin, and B-OHB on muscular efficiency is to “treat” a perfused rat heart under the following four conditions:
- Glucose alone (G)
- Glucose + insulin (GI)
- Glucose + B-OHB (GK)
- Glucose + insulin + B-OHB (GIK)
In fact, that’s exactly what this paper did. Look at what they found:
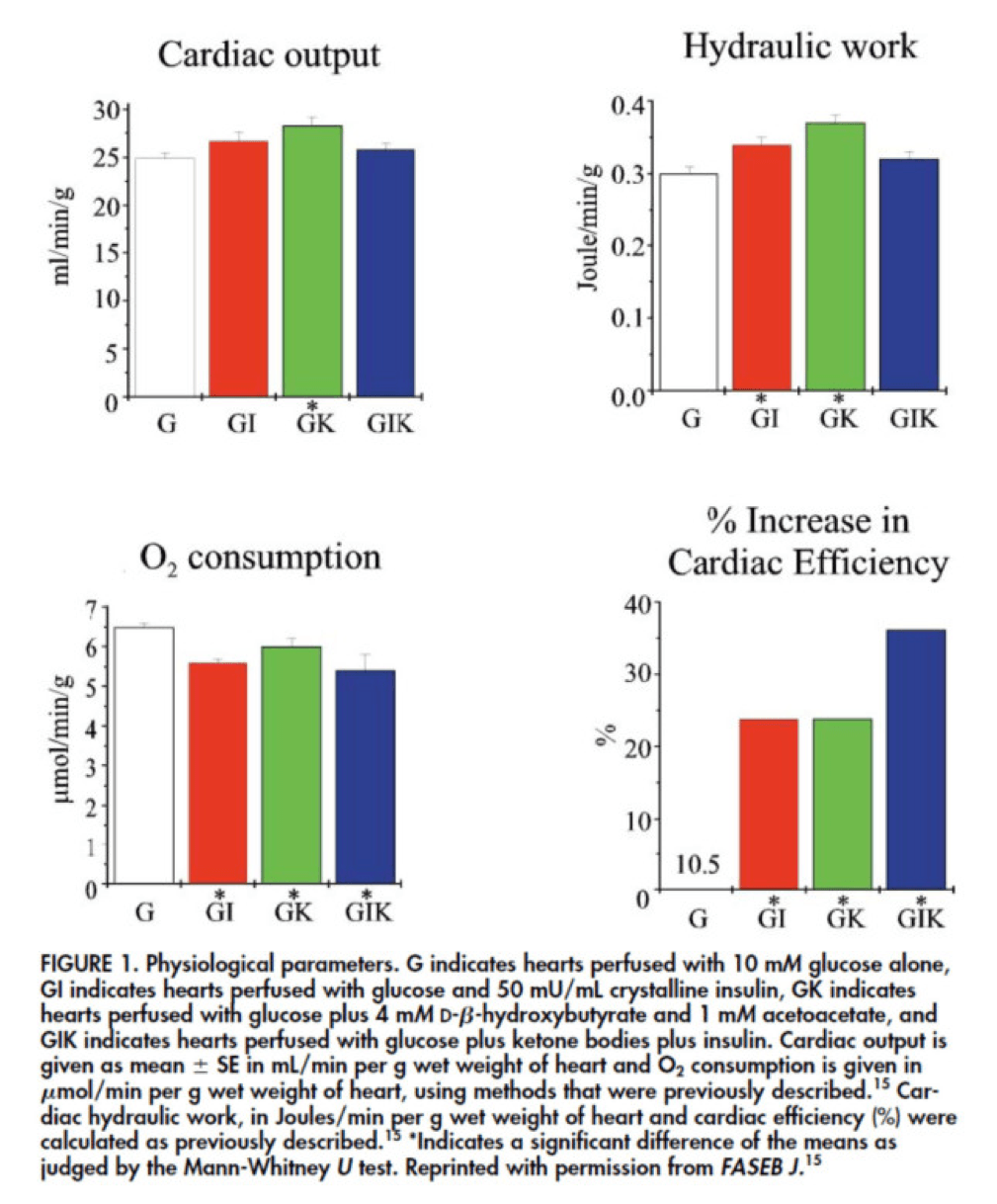
The upper two graphs in this figure show similar information, namely the response of cardiac output and hydraulic work to each treatment. (Cardiac output is pure measurement, as I described above, of volume of blood displaced per unit time. Hydraulic work is a bit more nuanced; it measures the mechanical work being done by the fluid.)
Adding insulin to a fixed glucose (GI) load increases both cardiac output and hydraulic work, but it’s only significant in the case of hydraulic work. Conversely, adding B-OHB to glucose (GK) increases both cardiac output and hydraulic work significantly. Interestingly, combining insulin and B-OHB with glucose (GIK) increases neither.
Oxygen consumption was significantly reduced in all arms relative to glucose alone, so we expect the cardiac efficiency to be much higher in all states. (Why? Because for less oxygen consumption, the hearts were able to deliver greater cardiac output and accomplish greater hydraulic work.)
The figure on the bottom right shows this exactly. If you’re wondering why the gain in efficiency is so great (24-37%), the answer is not evident from this figure. To understand exactly how and why adding high amounts of insulin (50 uU/mL) or B-OHB (4 mM) to glucose (10 mM) could cause such a step-function increase in cardiac efficiency, you need to look specifically at how the concentration of metabolic intermediates (e.g., ATP, ADP, lactate) varied in the rat heart cells.
This is where this post goes from “kind of technical” to “really technical.”
The figure below presents the results from this analysis. The height of the bar shows the fold-increase for each of the three treatments relative to glucose alone. To orient you, let’s look at a few examples. In the upper left of the figure you’ll note that GI and GIK both significantly increase glucose concentration in the cell, while GK does not. Why? The GI and GIK treatments both increase the number of GLUT4 transporters translocated to the cell surface so more glucose can flux in. GK does increase glucose concentration, but not significantly (in the statistical sense).
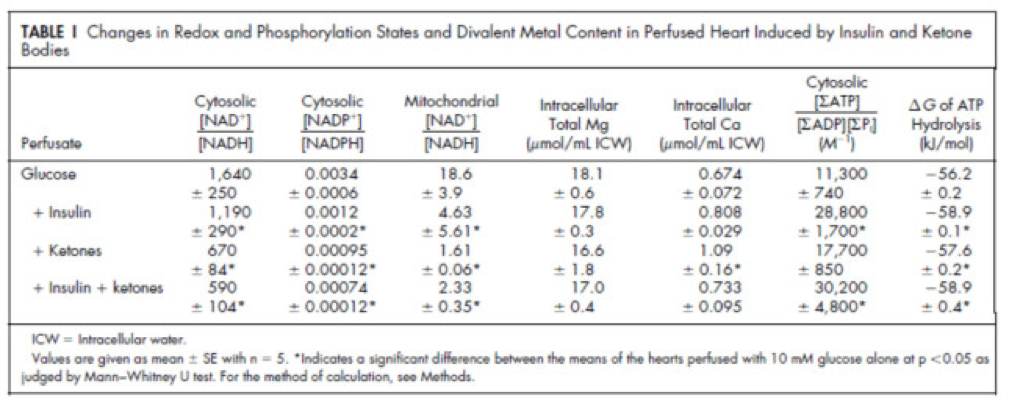
Table 1 from this paper, below, summarizes the important changes from this analysis. In particular, look at the last column, the Delta G of ATP hydrolysis.
I was really hoping to write this post without ever having to explain Delta G, but alas, I’ve decided to do it for two reasons:
- To really “get” this concept, we can’t avoid it, and;
- The readers of this blog are smart enough to handle this concept.
Delta G, or Gibbs free energy, is the “free” (though a better term is probably “available” or “potential”) energy of a system.
Delta G = Delta H – Temperature * Delta S, where H is enthalpy and S is entropy. The more negative Delta G is, the more available (or potential or “free”) energy exists in the system (e.g., a Delta G of -1000 kcal/mol has more available energy than one of -500 kcal/mol). To help with the point I really want to make I refer to you this video which does a good job explaining Gibbs free energy in the context of a biologic system. Take a moment to watch this video, if you’re not already intimately familiar with this concept.
Now that you understand Delta G, you will appreciate the significance of the table above. The Gibbs free energy of the GI, GK, and GIK states are all more negative than that of just glucose. In other words, these interventions offer more potential energy (with less oxygen consumption, don’t forget, which is the really amazing part).
To see what the substrate-by-substrate changes look like across the mitochondria and ETC, look at this figure:
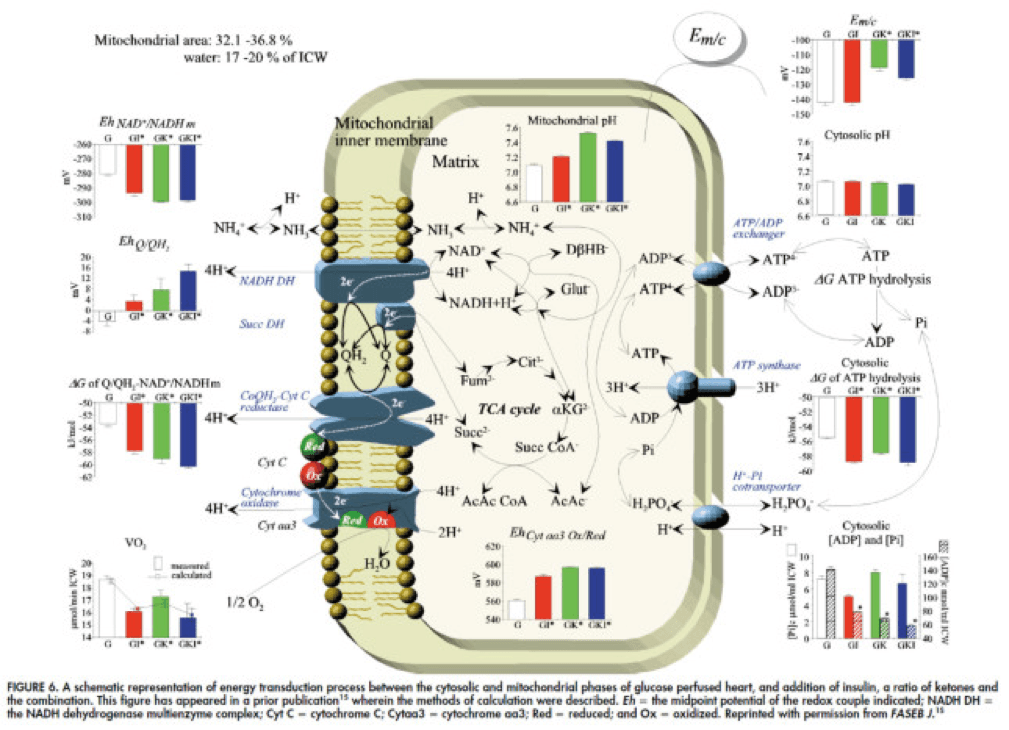
Though it is by no means remotely obvious, what is happening above boils down to two major shifts in substrate utilization:
- In one step the reactants NADH/NAD+ become more reduced (in the chemical sense), and;
- In another step the reactants CoQ/CoQH2 become more oxidized (in the chemical sense).
These changes, taken together, widen the energetic gap between the states and, in turn, translates to a higher (i.e., more negative) Delta G which translates to greater ATP production per unit of carbon.
Additional work, which you’ll be delighted to know I will not detail here, in fact shows that on a per carbon basis, B-OHB generates more ATP per 2-carbon moiety than glucose or pyruvate. As an aside, this phenomenon was first described in 1945 by the late Henry Lardy, who observed that sperm motility increased in the presence of B-OHB (relative to glucose) while oxygen consumption decreased!
Is there a reason to prefer GK over GI?
Yes. Recall that ketones make their way onto the metabolic playing field without going through PDH. Adding more insulin to the equation forces more pyruvate towards PDH into acetyl CoA. While B-OHB “mimics” the effect of additional insulin, it does so in a much cleaner fashion without the complex cascade of events brought on by additional insulin (e.g., decreased lipolysis) and, perhaps most importantly, avoids the logjam of impaired PDH due to insulin resistance (I’ll come back to this point in a future post when I address Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease). In essence, B-OHB “hijacks” the Krebs Cycle via a slick trick that lets it bypass the bottleneck, PDH. All the glucose and insulin in the world can’t overcome this bottleneck. It’s truly a privileged state and a remarkable evolutionary trick that we can utilize B-OHB.
Back to the original question…
Clearly, in the highly controlled setting of a perfused rat heart, ketones offer an enormous thermodynamic advantage (28%!). But what about in aggregate human performance? There is no reason to believe that therapeutic levels of B-OHB (either through nutritional ketosis or by ingesting ketone esters) would increase anaerobic power, since the anaerobic system does not leverage the Delta G improvement I’ve outlined here. Same is true for muscular strength. However, there is reason to believe that aerobic capacity and muscular endurance could be improved with sufficient B-OHB present to compliment glucose.
It turns out this has been demonstrated repeatedly in subjects ingesting ketone esters, developed by Dr. Richard Veech (NIH) and Dr. Kieran Clarke (Oxford). Because the results of their work have not yet been published, I can’t comment much or share the data I have, which they shared with me. I can say the ingestion of B-OHB in the D-isoform (the physiologic isoform), resulting in serum levels between 4 and 6 mM, did lead to significant increases in aerobic power and efficiency in several groups of elite athletes (e.g., Olympians) across multiple physical tasks maximally stressing the aerobic system.
Once published, I believe these studies will be a real shot across the bow of how we view athletic performance. It is very important to point out, however, that these studies don’t exactly address the most relevant question, which has to do with nutritional ketosis. In other words, ingesting ketone esters to a level of 4 to 6 mM might not be the same as de novo producing B-OHB to those levels. But, such trials should be forthcoming in the next few years. Personally, I am most eager to see the results of a ketone ester alone versus nutritional ketosis versus combination treatment, all to the same serum level of B-OHB.
The Hall Paradox
For the really astute readers, you may be saying, “Waaaaaaaait a minute, Peter…if ketones increase Gibbs free energy while reducing oxygen consumption, should this imply TEE goes down?” You’re right to ask this question. It was the first question I asked when I fully digested this material. If each molecule of B-OHB gives your muscles more ATP for less oxygen, you should expend less not more energy at the same caloric intake, right?
I was discussing this with Kevin Hall at NIH, an expert in metabolism and endocrinology. Kevin pointed out the error in my logic. I failed (in my question) to account for the energetic cost of making the ketones out of fat. Remember, in the experiments described above, the B-OHB is being provided for “free.” But physiologically (i.e., in nutritional ketosis or even starvation), we have to make the B-OHB out of fat. The net energy cost of doing this is actually great. According to Kevin, it is not generally appreciated how making ketones from fatty acids affects overall energy efficiency. Nevertheless, this can be examined by comparing the enthalpy of combustion of 4.5 moles of B-OHB, which is about -2,192 kcal, with the enthalpy of combustion of 1 mole of stearic acid (about -2,710 kcal) that was used to produce the 4.5 moles of ketones. Thus, there is about 20% energy loss in this process. Hence, the energy gain provided by the ketones is actually less than the energy cost of making them, at least in theory.
This suggests that being in nutritional ketosis may require more overall system energy, while still increasing work potential. In other words, a person in nutritional ketosis may increase their overall energy expenditure, while at the same time increasing their muscular efficiency. In honor of Kevin, I refer to this as the Hall Paradox.
Parting shot
Ok, if you’re still reading this, give yourself a pat on the back. This was a bit of chemistry tour de force. Why did I do it? Well, frankly, I’m tired of reading so much nonsense on this topic. Everybody with a WordPress account (and countless people without) feels entitled to spew their opinions about ketosis without even the slightest clue of what they are talking about. As I said in part I of this series, there is no bumper sticker way to address this question, so to say ketosis is “good” or “bad” without getting into the details is as useful as a warm bucket of hamster vomit (unless you’re Daniel Tosh, in which case I bet you can find a great use for it).
Next time, I’ll try to back it out of the weeds and get to more clinically interesting stuff. But we had to do this and we’re better for it.
Chemistry by Marcin Wichary is licensed under CC by 2.0





Hi Peter,
Just when I get fully subscribed to the low carb lifestyle, along comes this kind of post from a nutritionist that starts me to doubt the central hypothesis:
https://wholehealthsource.blogspot.com/2011/08/carbohydrate-hypothesis-of-obesity.html
Particularly troubling for me is the overall insulinogenic index of foods and the tribes/cultures that eat high carb but have low rates of obesity. How do you counter these arguments?
Ahhhh…I wrote a lengthy response to this and then lost it. Short response: Stephan raises some interesting points. It might be that these cultures don’t have the high amounts of sugar and processed foods we do. As a result they are likely much more insulin sensitive and therefore able to tolerate complex carbohydrates better. Read my post on this. I think it’s called something like Why Do Some Cultures…
Hi Peter,
I’ve transitioned from four months of ‘lower carbs’ of about 100 per day, to under 50 with a small calorie deficit while following Phinney and Voleks suggestions. My fitness goals are in weightlifting and bodybuilding- I’m currently at 13-15% body fat and when I get under 10% I plan to go into a ‘bulk’ aka calorie surplus plus heavier weights to gain muscle. Is there any evidence or even explanation for achieving significant muscle growth if I’m sourcing 100% of those additional calories from fat? Bodybuilding forums are a hot mess on this topic so I’m coming to you : )
Never got a response on this hey?
Hi,
I have recently come across your website and am finding it fascinating. It is certainly difficult to explain to people what I am considering doing, when it is ingrained in us that fats are bad.
I am currently doing a low carb, high protein diet which I guess is a step in the right direction. However, I have been trying to figure out what ratio’s I would need to adhere to (weigh 69kg, ideal weight is about 60kg).
Also, in looking at potential diet plans, I was struggling with keeping the protein low with the fat high.
Do you have any suggestions on the practicalities of keeping to a diet such as this?
Many thanks!
I don’t think anyone knows (or at least I don’t). I find this much more empiric, and dependent on individual variation.
Ok, so trial and error essentially.
Good news is I got some ketostix and I am officially in ketosis (but only just according to the scale, mid purple opposed to dark).
Will keep trying!
Great work. Okay, honestly I had to read post a few times to get it, and I have a medical background. You did a wonderful job putting it altogether.
Here are my questions related to ketosis and metabolism in general:
1) can triglycerides be converted back to glycogen in the non-starved person? In your post on lean cultures, use you say that turning glycogen into stored fat is a one-way street. Yet into ketosis 101, you do say that triglycerides can be made back into glycogen in a starved person.
2) reviewing energy you utilitization in exercising muscles – phosphagen system, glycolysis, followed by aerobic free fatty acid utilization – would a very lean person (on low carb 100-150 gm Paleo diet) end up in ketosis ( ie producing ketone bodies for energy), since they would have limited glycogen stores and not a lot of fat tissue to sustain exercise?
3) please comment on physiologic insulin resistance – the state where your insulin is low but your blood glucose tend to run on the high normal side – in a fit lean person without metabolic syndrome. Since insulin is an anabolic hormone, is the low insulin a health detriment? Is high circulating glucose all day long a cell toxin in this scenario?
Thank you.
So sorry, a follow-up question Peter.
In ketosis 101, you said that in the absence of substrate (in other words no FFAs to be turned into Acetylco-A to go through the Krebs cycle) the ketone bodies are formed,. But if your diet is primarily fat, don’t you always have free fatty acids to make into acetylco -A and therefore you would not begoing into ketosis? I am sure that there is a readily available explanation in the material you wrote, but I cannot bridge this gap.
Thanks again.
In the absence of glucose (turned into pyruvate into acetyl CoA)
Dr Attia – What’s the best post-workout food for optimal muscle growth while still preserving a largely ketogenic state? Can we make enough glucose from gluconeogenesis (via glycerol backbones of FAs or carbon skeletons of amino acids, e.g.) to trigger glycogenesis or do we need to consume carbs for growth? Seems like this process would be too slow (if it even happens) to allow adequate recovery after depleting muscle glycogen stores. Love to hear your thoughts – JS
Not really my area of expertise. I try to consume about 25 gm of why protein immediately post resistance training, based on the limited data I’ve seen.
https://forum.bodybuilding.com/showthread.php?t=7620681&page=1
don’t know anything @ this treerollins poster, but the biochem seems fairly sound.
food for thought…
How to begin….. your diplomatic rebuke, send me back to the books, and most importantly to a post which I neglected because I thought from the title that it would only lead me to product information (“Superstarch”). How I was wrong! I encourage all of the folks new to your blog to spend the time to listen to the embedded video – a wealth of information. I now see where my questions reflected my lack of understanding, my apologies.
Can I still impose on you to answer the third question in my submission (dated March 9), in specific about physiologic insulin resistance in a low carb dieter? I never even knew such a condition existed until I read about it on both the Hyperlipid and Ketopia websites. I am trying to understand the mechanism by which insulin levels are low but glucose runs high through the day (increase A1C) in the non metabolic syndrome person – if you can supply the mechanism, I would be appreciative.
Thank you for your time.
Hi Peter,
I think there is no need to answer to my question about physiologic insulin resistance, it appears to me that all of the available information pertains to VLC ketoadapted diets, nothing to find on LC Paleo type, 100-150gms CHO/d. I did read the short term analysis – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/expphysiol.2006.033399/abstract – but really did not answer my query.
My goal is to find a framework to understand the effects of a LC Paleo diet, so that I can recommend it to even T2dm patients (I’ve discussed it with nondiabetics, both lean and obese) and follow/understand their serum profiles. I cannot get support from endos and Diabetes Centers in the GTA – they all follow the Canada Food Guide, with lots of grains. I am not yet comfortable suggesting a ketogenic diet, without the support structure of the conventional medical community.
I thank you for your patience with me, and your time, I am clearly frustrated with my inability to make inroads and appeal to open minds in the conventional medical community.
Hi Peter…. Hoping to get your thoughts on this:
I was wondering your take on Dr. Jack Kruse’s blog on there being this PPP pathway (Pentose phosphate pathway) for superhuman performance. Using no or little carbs or a ketogenic diet among other things.
https://www.jackkruse.com/emf-4-why-m…r-performance/
Do you see merit in this and are you discovering this in your own training?
I can see the fat adapt lower carb using fat as fuel for aerobic power and sustainability. How about in power athletes as well once fully adapt?
Just wanted to hear your take on it.
One of Jack’s response’s to my asking about it and how long it takes to see real results; “within 3 yrs you wil kill people if you stick with it”.
Not sure how long you have been at it and if you are starting to see a switch in your anaerobic and strength power as well. I was told it takes 2-3 years to truly develop and be in this pathway to have the benefits of it.
What is your experience and also applied not only to endurance athletes but strength, power and higher intensity performance as well. I just don’t see any world class athletes “yet” using this approach and smashing records or achieving great performance results.
I am still trying to understand…. I know for you it is working great for an endurance athlete…. Is this the case for any athlete; power, endurance, HIIT, strength, etc. in your experience?
Thanks in advance for your response…..
– Dan
I have no idea.
Thank you, Peter, for all this great information!
I have been reading your blog and just recently started a ketogenic diet and I had a few questions. Is there any research, that you know of, that show a connection between endometriosis and a ketogenic diet improving the symptoms? Over a year ago I had to have an ablation done because of such heavy menstrual cycles (I lost nearly 3/4 of a pint of blood my last cycle). That effectively took care of the heavy bleeding and I have not had a cycle since….But before the surgery, I had been doing the endometriosis diet and had eliminated dairy, wheat, soy and red meats from my diet. When I did all that my pain was greatly diminished and I was able to see the correlation between my terrible hot flashes and mood swings to these foods, especially dairy.
Now, this past week I’ve noticed something quite incredible. Last Sunday evening I began my ketogenic diet and it took me a few days to get the hang of it (I started the diet initially to lose weight). Within 48 I was experiencing terrible ovarian pain and the area was quite tender to the touch but as soon as I upped my sodium intake and added some potassium rich veggies that soon subsided. By the time I reached ketosis, the pain had totally decreased. But what was more interesting than that was I decided to try some dairy and some red meat since I was running low on groceries. I figured dealing with a few hot flashes wasn’t that big of a deal as long as I could keep on my ketogenic diet until I got to the grocery store. What I found out is that I no longer have the hot flashes that usually follow the consumption of these foods. I guess I should mention I’m only 34 and I’ve had two children with a total of 7 pregnancies. I currently weigh 160 pounds and I’m 5’9 ( I lost anywhere from 5-8 pounds this week….I never weighed myself before starting the diet and only began to weigh myself a few days into it). I’ve had no other health issues and no doctor has ever brought to my attention any issues when I had blood tests performed.
I’ve been looking everywhere on the net to see if other women have experienced relief from a ketogenic diet and if there are studies to back it up. When I went into surgery, over a year ago, my doctor wanted to do a hysterectomy and I refused. I just want to make sure that I never have to take that route and I know diet is a giant contributing factor to endometriosis. So any information you could send my way would be fantastic!
Sorry, Malinda, I’m not knowledgeable on this topic.
Hi Peter,
I read here that ketones can’t completely replace glucose as an energy source for the brain:
https://www.proteinpower.com/drmike/ketones-and-ketosis/metabolism-and-ketosis/
I assume this is why it’s necessary to maintain blood sugar within a homeostatic range. If this is true, what parts of the brain absolutely need glucose to function?
Thanks,
Tyrone
Tyrone, I’m not sure if it’s true that the brain can’t subside on B-OHB alone, but a better point is that we never have to, even in complete starvation (TG –> FFA + glycerol; the FFA get turned into B-OHB; the glycerol into glycogen). So the point is sort of moot. We always have some glucose for our brain. In complete starvation or significant NK, the balance is 50/50 +/- 10% either way.
Looking for a little advice, I’ve been in Ketosis for over 2 weeks, urine ketones and blood tests all consistent with Ketosis. But I’ve GAINED weight! I feel good, my waist is already looking good, brain fog gone…I attribute all to my beneficial diet changes. Hope one of you can give me some reassurance.
Can’t troubleshoot this way. Hopefully Part III of series helps.
Dr Attia
Did you ever get an answer from Dr. Westman to these questions
“The question we don’t know the answer to is if an LDL-P of 2,000 in someone who eats no carbs is the same as an LDL-P of 2,000 in someone who does. I had breakfast with Eric Westman today and we discussed this topic. Eric makes a pretty compelling case that these 2 states are not, in fact, the same thing. I think we can safely say we don’t know the answer. At least I don’t. I’ll keep looking for clues, though.
I completely agree with Eric’s assertion (in fact, I’m having breakfast with Eric in an hour). This brings up a much larger question that I’m sure I will detail more closely in this series: It is possible that all of the risk stratification we have for heart disease is predicated on someone consuming a normal Western diet? Furthermore, is it possible that once the body stops relying on glycogen and turns over to metabolic pathways of ketosis that the “numbers” we target as “normal” are irrelevant? I think I know the answer for some physiologic parameters, but I’m still trying to develop my “universal theory” uniting it all.”
We are extremely curious.
Still be “hotly” debated in this circle. This will be covered in Part X of the cholesterol series, I expect.
Hello Peter,
The work you are doing is truly inspirational. I’m a 22 year old from London, UK spreading the word on Low-Carb (to those who listen of course).
Anyway, I would just like to say I adopted the Low-Carb lifestyle back in September 2012. I have become an absolute advocate. I feel so good and my concentration levels are unbelievable (sitting my finals at University soon so that’s helpful). I would like to share that I conquered the London Marathon 2013 (4 hours and 36 seconds) and all of my training and racing was done low-carb. There was absolutely no carb loading, lucozade, gatorade, gu or gels involved whatsoever! I had my daily egg,bacon and avocado on race morning. I consumed a packet of Superstarch 45 mins before the marathon ( 26g carbs or 110 calories) then another pack during the marathon from around mile 10 onwards. I didn’t hit a wall.. I didn’t crash and burn like many people expected me to. I powered on through with only 52g of carbohydrates (220 calories) in the form of Superstarch . A calories deficit supposedly in the region of 2400 calories. Fat burning machine?.. Yes sir, I sure am!
Recently discovered your web site. It is extremely well done.
Please consider adding a section covering references; particularly with respect to books.
I realize that you embed references/links in your essays; however, in some instances particularly when authors have multiple publications, a bibliography would be helpful; e.g., Phinney and Volek … yes but which of their books?
Hi Peter,
I absolutely love your insightful posts. I’m a middle-distance runner myself (800m-10km) and currently just training my aerobic system with easy,slow running whilst recovering from achilles tendinopathy. I wanted to ask you whether you think adapting to ketosis and utilising fat as fuel during my base training, before eating more carbohydrates prior to and post-competition would be a good idea? I’m 18 years old and just eat an unprocessed, balanced diet, but want to eschew grains and trial the ketogenic diet. How long would you say it takes to fully adapt?
Thanks a lot Peter,
Jonny.
Hard to say without knowing much more. Full adaptation takes a while, probably on the order of 2-3 years if my experience is representative. The tough thing with your events is the span from pure glycolysis in the 800 to pure (just) sub-threshold in the 10k. Former is not likely helped by ketosis (except for the aerobic base work in training). Latter is likely helped quite a bit.
Hi Jonny,
FWIW, I think you should look at Jack Kruse’s work on cold thermogenesis to further enhance your adaption and performance.
I have a question I am hoping you can help me with. I am a 41 year old female, with insulin resistance, PCOS and hypothyroid. I am obese with around 40kgs to lose 😮 I have been following LCHF for a few weeks and have lost 4kgs. My daily macros are around 1400-1500 calories – 75% fat, 20% protein, 5% carbs. I eat no grains and no refined sugar (very, very little rice malt syrup or coconut sugar). Ketostix show i am in ketosis. My question….Around 12 years ago I had my gall bladder removed. It suddenly occurred to me that the LCHF diet might not be for me because of this???? It would be great if you could help me out with this. Should I be making allowances for the fact I have no gall bladder?? Many thanks in advance!!
It may require eating less fat in one sitting, since the GB is a reservoir for bile. But it does not diminish your ability to produce bile and emulsify dietary fat.
I’m new and catching up, I missed what TEE means can someone please define for me? It would go to a long way in understanding this article. Thanks so much!
Andrea
Sorry, means total energy expenditure. I think I defined these terms the post “Good science, bad interpretation.”
Peter,
I have a question that you may or may not be able to answer. On the ketogenic diet you have to replace more salt. It is logical baby that the Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone system would be working overdrive? Particularly in the morning before my Bouillion?
The reason I ask is because I take my heart rate variability every morning. I analyse it with regards to VLF, LF and HF. Since I have been ketogenic I have noted a very very high VLF component, in the literature this is believed to be related to activity in the RAS. Does this logic make sense? Could this indicate I need more salt to calm my RAS down?
Tom
Yes, it’s possible, in the absence of sufficient salt that RAS is working hard to preserve sodium, though there seems to be adaptation to this over time. I rarely require bouillon any more, though I once couldn’t get through the day without it.