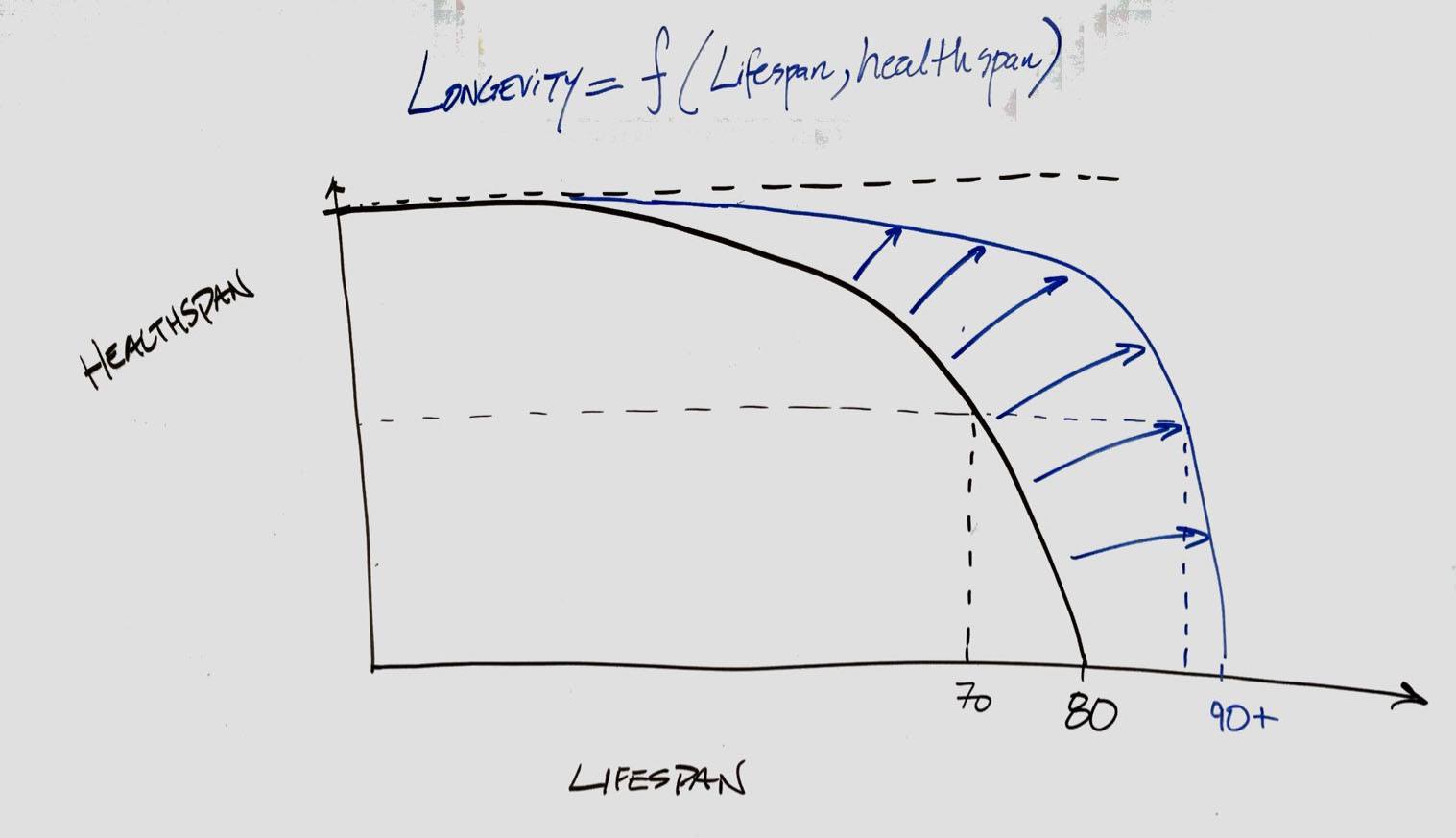
My clinical interest is longevity, which is a function of lifespan and healthspan; In math parlance, longevity = f (lifespan, healthspan). Lifespan is pretty easy to define. It’s the number of years you live. Healthspan is intuitively obvious, but a bit harder to define. For simplicity, let’s agree that healthspan is a measure of how well, not necessarily long, you live. Further, let’s agree that one without the other—long lifespan with poor healthspan or short lifespan with rich healthspan—isn’t what most people want. This has the makings of a complex, nonlinear, multivariate optimization problem.
The figure below is from my office whiteboard last week. I was explaining the relationship between lifespan (x-axis) and healthspan (y-axis) to one of my patients. My goal is to move the black line to the blue one. Live longer (more x-axis) and live better (altered shape of decline curve).
I’m in the (very slow and time consuming) process of writing a book on this topic, which is really two books in one—the science of longevity and the “art” of it, the latter being a nuanced discussion about how one applies said science (most of it in animals) to the species of interest—people. If you don’t spend much time in the longevity literature, this distinction may not seem warranted. If you do spend time in said literature, it will be obvious why such a distinction is necessary.
Lifespan, at the first order, is driven by how long one can delay the onset of atherosclerotic disease (CHD, CVA), cancer, and neurodegenerative disease. Delay the onset of these, and you live longer. It’s a probabilistic truism. Obviously, I will explain this in great detail at the appropriate time, but I don’t want to focus on this topic today.
Healthspan, in its most distilled form, is about preserving three elements of life as long as possible:
- Brain—namely, how long can you preserve cognition (i.e., executive function, processing speed, short-term memory)
- Body—specifically, how long can you maintain muscle mass, functional movement and strength, flexibility, and freedom from pain
- “Spirit”—how robust is your social support network and your sense of purpose
In this post, I’d like to focus on one subset of healthspan: item #2—movement. But before I do, a brief digression will be helpful.
The hack—Darwin meets MacGyver
Evolutionary biology can, at times, provide a helpful framework for longevity. Our need for sleep and our resilience to short-term food deprivation are just two examples of traits that served our interests tens of thousands of years ago and continue to do so today. Some of the interventions that can make you live longer and live better will find their foundation in understanding evolutionary biology. But many won’t. That is, many things I (and others) argue are necessary for longevity don’t really have an obvious foundation in evolutionary biology. Why?
Enter “the hack.”
A hack is something we do that gets around a problem, even if it’s not especially elegant. A patch might be an easier way for some to understand what I mean (cf. software patch). The hack can be elegant, the hack can be cumbersome, but its purpose is the same—something is getting in the way of a desired outcome and we need a workaround.
When I talk with my patients I try to differentiate interventions I propose as “evolutionary sound” or as “hacks.” Inasmuch as this framework is helpful, let me expand.
Our evolutionary ancestors were primarily concerned with survival. There was no survival more important than reproductive survival—ensuring you lived long enough to reproduce. Natural selection would prioritize short-term survival over long-term survival or quality of life. [As a very interesting, but too-nuanced-for-now aside, the evolution of APOE genes from the E4 to E3 to E2 variants may be great examples of this…yes, this will be discussed in the book, space permitted.]
Take stress response as an example. The stress response was an essential part of evolution. Without it, fending off an animal trying to attack you, or hunting for food in a state of starvation would not have been possible. Nothing about our evolutionary development selected for, or rewarded, equanimity. Our ancestors probably did not have the luxury of inner peace. It’s also not clear if it would have been necessary, or even helpful. But I argue that our current environment places sufficient non-evolutionary stress on us, and, as such, a hack that separates us from this stress is, indeed, helpful. Furthermore, we now have the luxury of aspiring to things our ancestors could never dream of. They were preoccupied with reproducing and not dying; we aspire to play with our great grandchildren, we machinate on our legacies, we argue about if the Oscars are really inclusive enough.
Years ago, when I read Jared Diamond’s magnum opus, “Guns, Germs, and Steel,” I remember thinking to myself how horrible it must have been to have lived even as recently as just a few hundred years ago, let alone a few thousand years ago. It really had a profound impact on me, though it was not the central thesis of his book at all. I realized that on my “worst” day—lost my cell phone, got a speeding ticket or had a fender bender, missed my flight, got food poisoning from some bad sushi—it didn’t really matter. Technology and civilization took a bunch of really acute problems—lethal infections, starvation, trauma, war, for example—and traded them for more chronic ones—lower back pain, heart attacks, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. I’m not minimizing the latter. These problems matter, but evolution didn’t confront them and therefore we can’t readily turn to evolutionary insights for solutions. Parenthetically, it might not have been as miserable as I imagine, namely because our ancestors didn’t know any better. It’s not like they would have “missed” Tweeting on their smartphones or racing around on their carbon fiber bikes, lamented the loss of their favorite sports team, or missed the pleasure of sipping neat Don Julio 1942.
Think about what Peter Parker’s uncle said to him shortly before he was killed, “Remember, with great power comes great responsibility.” I think of our modern lives as a great power, or a great privilege, to be more accurate, I suppose. I would never want to go back and live as my ancestors did tens of thousands of years ago (or even a hundred years ago, though it might make for a nice vacation) and so I should pause for a moment and acknowledge the complete privilege of living today in this incredibly narrow sliver of time. I love the internet. I love that agriculture and crop domestication have allowed me to live in civil society with dense populations and no fear of starvation. I love that a simple antibiotic can save my life from a formerly lethal infection. I love being able to sit down in a car or airplane, and I love the freedom those machines have brought me.
So if these examples of things I love are some of my great privileges, what are my great responsibilities? This is where hacks come in. We need hacks to prevent these great privileges from killing us—slowly—which they will do if we’re not deliberate. What are my hacks? A bunch of things that make virtually zero evolutionary sense but, if bolted onto my modern life, can give me—if I can thread the needle correctly—the best of both words.
Meditation, intermittent fasting, heavy compound joint and hip-hinge training, intense interval training, body work, supplements, drugs, introspection, sleep hygiene. These are my hacks. Let’s focus on one hack, in particular—movement preparation.
The savant of movement
I met Jesse Schwartzman through a mutual friend. After our first workout together I was blown away, but it wasn’t the workout that impressed me, it was the preparation routine Jesse put me through, prior to making me puke, that impressed me. I’d never felt more ready to move. Jesse’s formal bio is at the bottom of this page, but I just call him the savant of movement. One day Jesse and I were having coffee and he commented at how annoyed he was by the endless stream of “heroic” tweets and IGs of super-humans doing one-armed acrobatics or whatever the stunt of the day is. He commented, astutely, I noted, that the world needs another super-human trying to convince the rest of us we should be like him/her like it needs another dictator.
What we actually need are examples of how real people can be empowered to preserve muscle mass, move functionally, maintain freedom from pain, and be the best athletes of their lives. An “athlete-of-life” can hip-hinge, squat, carry, shift, push, pull, rotate, and anti-rotate with confidence and fluidity. On a deeper level, one should also re-connect to their childhood movement patterns, before the toll of life and technology wreaked havoc. We need to re-learn how to roll, crawl, and hang, which are patterns that can release the “brakes” from our everyday movement that sabotage strength and lead to pain and injury.
Watch a 2-year-old squat and you’ll know what I mean. They look like perfect little power lifters. By the time they are in grade school, and they’ve been sitting for hours a day, the first thing I see is tight hips. [Picture below courtesy my friend Pat Jak, also obsessed with correct movement.]
To that end, we decided to make a video of the exact warm-up sequence Jesse put me through so I could share it with my patients. If they (and you) find this video helpful, we’d like to produce more of these covering more specific topics, such as how to protect/ build/ rehab knees/ shoulders/ lower back, etc.
Before diving into the videos, I know at least one person is reading this and thinking, “What the hell is Attia talking about? He’s the king of doing stupid stuff like flipping 450-pound tires, swimming 12 hours, doing Tabata deadlifts…” And you’d be right. I do/did a lot of stupid stuff. But I always differentiate the stupid (“super-human”) stuff I do from the longevity drivers. My pet peeve, and that of Jesse, is that good people are misled by the heroics of big-personality super-humans who lead them to believe they need to do these things to live better. In reality, it’s almost always the opposite. You don’t have to do super-human feats to have great healthspan and, by extension, longevity. But you do have to do some very deliberate things to overcome our civilized environment. So while I call Jesse the savant of movement, he prefers to call himself the anti-super-human teacher.
Below are four videos, a brief introduction, and one video for each of the three stages of the warm-up:
- Tissue preparation
- Muscle activation
- Dynamic preparation
In addition, we’ve put together a “tear sheet” for each of the three stages in case you want take them with you to the gym until you commit to memory.
I should point something out, since I know it will come up. With the recent publication of Tim’s book, Tools of Titans, I’ve been getting a lot of requests to make a video of my so-called “Jane Fonda” routine. In Part II of the videos, below, I do a glute med activation exercise, but it is not the full sequence I describe in Tools. That’s ok…the form that Jesse and I demonstrate, coupled with the description in the book, should be sufficient to get you through the full routine of seven movements. For the purpose of movement preparation, one only needs a bit of activation (hence the vertical plane, only). What I describe in Tools is a therapeutic routine I perform once or twice each week.
Lastly, and most importantly, I want to thank Elliot Stern and Kelly Choi for shooting, producing and editing these videos from start to finish. If you could only see the outtakes…
Introduction
Here is direct link: https://youtu.be/ZVUQb2G_Mvw
Here is link to tear sheet, summarizing all three parts
Part I: Soft tissue preparation
Here is direct link: https://youtu.be/zdRgJpxifqA
Part II: Muscle activation
Here is direct link: https://youtu.be/JElEpnVH35Q
Part III: Dynamic preparation
Here is direct link: https://youtu.be/BGrw5z1SjtA
Jesse Schwartzman, MS, RD, ACSM CPT, holds a Master’s Degree in Nutrition and Applied Exercise Physiology from Columbia University, and is a Registered Dietician. Jesse, along with his wife Patty, currently owns and operates Fit4ward in NYC and the greater Fairfield County, CT, where he manages and engages in deeply personalized work with his clientele in all aspects of health.
Early on in his career, the importance of adopting lifestyle behaviors to support exercise and nutrition goals became a fundamental focus of his work. Joint mobility and tissue health, proper fascia and nervous system regeneration, fueling techniques, sleep and recovery, identifying asymmetries, and proper neuromuscular motor patterns are incorporated with every individual.
Jesse now has over 10 years of experience in the health and wellness industry in one on one personal training, nutritional counseling, health coaching, group workshops, and the corporate setting. Jesse previously trained clients at the highest certification level at Equinox Fitness Clubs, and managed Equinox’s most elite trainers and exclusive clientele in the Tier 4 Program at the “E” club.
Photo by Hidde Rensink on Unsplash







My chiro told me he was not familiar with the term “locked long” and that he wanted to understand the physiology behind rolling the hamstrings side to side. Any insight?
Some fascial lines are chronically pulled long while others are pulled short. Hamstrings are pulled chronically long as they are overstretched from gait, quads are locked short. Extensors are generally locked long while flexors are locked short.
Thanks for your reply Jesse!
I am doing it after the warm up. It is not really “exercise” as I only do what is called a “health bounce,” which means my feet do not leave the mat. I push up from my heals that remain on the mat. There is some good research on this – you might want to check it out, specifically with NASA for returning astronauts. This bounce is for stimulating the lymphatic system. I have read that they are introducing this in nursing homes for older people – more beneficial than treadmill for example. And, they can start slowly with 2 minutes or so.
I do 15 minutes then my kettle bell series with a light bounce again between sets. I wonder if I would be getting the impact that you describe based on the fact that I am not leaving the mat. Also key is that I have a high quality mat that does not have a big give in it – there are many brands that do harm, so I’ve read. I use the Cellerciser. There are bungee cord mats that have too much give and do not the g-force that one wants – again based on the research.
If you ever do look into it, I’d love to hear your thoughts.
Thank you again for doing the vids – I cannot tell you how many friends and clients I have already sent it to. And, after one session only I slept better (doing it in the evening) than I have in months! I can somewhat isolate this as the cause, I believe.
You and Peter are the best!!!
Sheila
The NASA research on rebounding. This is from Wikipeidia so, not sure if they are capturing it correctly…
NASA study and scientific support generally[edit]
The single most important and most frequently quoted scientific research study on rebounding was conducted in 1980 through NASA by A. Bhattacharya, E.P. McCutcheon, E.Shvartz, and J.E. Greenleaf; Biomechanical Research Division, NASA-Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, in cooperation with the Wenner-Gren Research laboratory, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky.[9] The key findings for this study include the following:
“.. . for similar levels of heart rate and oxygen consumption, the magnitude of the bio mechanical stimuli is greater with jumping on a trampoline than with running, a finding that might help identify acceleration parameters needed for the design of remedial procedures to avert deconditioning in persons exposed to weightlessness.”
“The external work output at equivalent levels of oxygen uptake were significantly greater while trampolining than running. The greatest difference was about 68%.”
“While trampolining, as long as the G-force remained below 4-G’s, the ratio of oxygen consumption compared to biomechanical conditioning was sometimes more than twice as efficient as treadmill running.”
“The G-force measured at the ankle was always more than twice the G-force measured at the back and forehead while running on a treadmill.…While jumping on a trampoline, the G-force was almost the same at all three points, (ankle, back, forehead) and well below the rupture threshold of a normal healthy individual.”
” …averting the deconditioning that occurs during the immobilization of bed rest or space flight, due to a lack of gravireceptor stimulation (in addition to other factors), requires an acceleration profile that can be delivered at a relatively low metabolic cost….for equivalent metabolic cost, and acceleration profile from jumping [on a trampoline] will provide greater stimuli to gravireceptors.”
Hi dr. Attia,
First of all I would like to thank you for the great service you are doing for me and all of your other readers in this blog and this specific post.
In your “hacks” list you mentioned Supplements!
I wonder if you mind sharing what supplements are you taking?
I know that it might be very different from one person to the other and I promise you I won’t take your words as medical advice… 🙂
Thanks a lot!
Aviv from Israel (Big fan of your work!)
Episode 65 of The Tim Ferriss Show
I know you’re in San Diego and New York and those are too far for we midwesterners to reach. So how does one go about finding a doctor in, say, Minneapolis who does what you do (medical practice wise) and isn’t going to just regurgitate the “low fat, whole grains, lots of fruits for energy” mantra that’s shortening our lives?
It is based only on my personal experience and a few others.
-When done regularly, a foam roller is not enough and will feel too soft. More precise and hard tools will be needed such as anything solid and one with a plane base for stabilization.
I use personally a small glass jam for tensor fasciae latae and a golf ball for the finish for precision. Only with such tools you will really understand how much tension you still have in those muscles.
– Up to now, I was able to elicit LTR(Local twitch response) only with “hard” and small tools most of the times.
An indication of the location a Mtrp (myofascial trigger point) can be seen when a muscle exhibits a local twitch response.
A LTR is an involuntary twitch of the muscle that is thought to reduce spontaneous electrical noise at the motor endplate leading to greater tissue extensibility.(Chen 2001, Hsieh 2011, Chou 2011)with also short-term positive therapeutic benefit. (Hong 1994, Rha 2011)
And you will feel that release of tension and pleasure immediately after the LTR. It is really something to try !
But do not get overboard or you may end up with bruises or pinched nerves in some location(I experienced both)
Omar
Thank you so much for these videos. I had an lightbulb moment a few years ago – my Mom (in her 70s) and I were in my garage and she was unable to step up onto a box about two feet up. I was shocked. When does this happen I thought and how can I not let it happen to me? I’m in my mid 50s with insulin resistance challenges and not much of an athlete, but I can still climb and go into a full squat (like a child). I plan to hang onto this mobility and not let it slip away in the next decades.
Amazing stuff! Production quality is great, but I was hoping for some Borat impersonations, maybe next time?
I almost did this whole video in my Borat lime green mankini…
“Healthspan”: good term. I also like the concept Andrew Weil promotes in his book Healthy Aging: compression of morbidity.
(Disclaimer: I’m not a fan of everything promoted by Dr. Weil, but I do like that term.)
Cheers!
Hi, Peter. I haven’t read your point of view about K. Hall-NuSI published keto study. Did you write anything on the subject? I would like very much to know your opinion about results and author’s conclusions. Thank you.
Nope.
I am also looking for thoughtful and sober responses to Hall’s study Dr Hall presents a very well conceived experiment
His data and his conclusions are not easily dismissed
I believe others have offered what you are looking for.
Peter thank you for all you do.
Thank you, Henry. Glad you enjoy it.
I’m also interested in your opinion about Hall-NuSI study, Peter. Please, do not bother, we admire your work and value your conclusiones in a special way.
I wasn’t planning to bother… 🙂
The videos are excellent. Thank you for producing and sharing them. I’m even using the warmup routines alone on my off days just to feel refreshed.
– Dave
Thank you, Dave.
Hi again Peter: Just listened yesterday to your January podcast with Jocko Willink. I loved it! I especially pricked up my ears at the following statement you made (I’m paraphrasing): “I don’t like to talk much anymore about nutrition, because nutrition is a pseudoscience masquerading as a religion or dogma.” (Or maybe you said it’s a “religion masquerading as a pseudoscience.”) You also said your thoughts on the topic have changed in the last couple of years and then went on to share your present thinking.
THANK you for saying this. As someone who has studied and thought about nutrition for 35+ years and has observed (unscientifically) people’s eating habits over that same time period, that has long been my impression. (I have a BS in the topic but never became an RD.) There’s no one precisely right way to eat for every body (I’m using two words there deliberately). There are a handful of general guidelines that seem to hold true for promoting health no matter who you are, but that’s about it. Yet many people become so dogmatic about their food-related beliefs.
I’m really hoping you’ll develop this idea in a future blog post. Or maybe it’s a topic you’ll explore in your book. (I sent you an email about your book, btw.)
Thanks, as always, for all you do! Cheers.
Edit to clarify:
I hold a BS in the *subject* of nutrition and food science.
Easy to confuse plain old BS in nutrition, huh? 🙂
Glad you appreciate it, Kelley.
Hi Peter,
a little off-topic but is it worthwhile to do a medium fat, medium carbohydrate diet? So I was thinking to lower daily carbs from 240/250 grams to 120-130 grams and add more fat to my diet instead.(I’d like to keep some carbs for various reasons) Or is lots of fat only healthy if you are mostly in ketosis? (I have T1D btw)
Dear Doctor Attia and Mr. Schwartzman,
Thank you so much for these videos. As as 65
year old, I find them wonderfully useful.
Happy to hear, Mike.
Great stuff. Thanks!
Any thoughts on what a proper cool down should look like after a workout?
A proper cool down Is more about getting the nervous system back to parasympathetic mode. I would lay on the floor and put your hands on your belly to focus breathing in that area. 5 count inhalation, 5 count hold, 10 count exhalation. Do for 5 minutes. I also like a stretch called Bretzel 2.0. But don’t just crank and stretch muscles. You won’t improve flexibility, and could damage the ligaments long term. An effective cool down is about getting the heart rate down gradually, and getting proper circulation back to your tissue..
Hey Peter,
I sent an email through the contact form, but figured I would post a comment as you respond to those more frequently. We share a similar story–I was an engineering undergrad, then had a change of heart and went into medicine. I did a neurosurgery residency at UT Southwestern but was unable to finish due to a seizure disorder caused by multiple concussions from martial arts. I completed an anesthesia residency at Hopkins not long after you were there. I took time off between neurosurgery and anesthesia to treat a hydrocodone addiction. I finished anesthesia residency extremely overweight and found nutrition and fitness after residency and now am an active crossfitter, endurance athlete and nutrition fanatic. Like you, I enjoy the practice of medicine, specifically anesthesiology, but am most passionate about the type of medicine you practice. I wanted to reach out to you to possibly seek some mentorship in getting involved in the type of medicine you practice. Hope to get to talk to you. I know you are extremely busy, but was hoping you had some time for a fellow Hopkins grad. -Mark
Back to CGM.
Apologies if it has been highlighted before. As the CGM does not directly measure glucose levels in the blood, it measures glucose levels from the fluid under the skin (interstitial fluid), not sure if I have got the technical name for the fluid right. So, there is a time delay for the blood glucose levels to appear in the fluid which the CGM is sensing. Apparently this time delay is between 20-30 minutes and the CGM would be showing the glucose levels that were 20-30 minutes ago in the blood. Also, CGM needs to be calibrated with the blood glucose monitor otherwise it will keep moving further and further away from actual blood glucose levels.
Hi Peter, I’ve been reading your blog for over a year and having a great time with it.
1) I imagine you’ve read born to run?
2) can I really eat all the bacon, sausage, fat I want? It makes me feel great but I am worried about going against accepted knowledge.
Thanks for your blog. It’s always a great read.
Colin